
- 1 January 2024
Qualitative Data Analysis with ChatGPT
Can qualitative data analysis be done with ChatGPT? The answer is partly yes. We will prove it to you in this article. But first, let’s give a brief overview of what quantitative and qualitative data analysis.
Quantitative and Qualitative data analysis are the two main analysis approaches used in research. The two methods follow very different paths from data collection to reporting. In quantitative data analysis, data obtained using numerical and large sample sizes, independent of the researcher’s interpretations, are processed through statistical analysis and reported and presented in graphs, charts and tables, while in qualitative data analysis, non-numerical data such as participants’ experiences, perceptions and emotions are analyzed in the context of common themes and patterns that are open to interpretation in a highly flexible manner and reported and presented in the form of findings, stories, quotes and explanations.
In the light of this brief information about the two analysis methods, it would not be wrong to say that quantitative data analysis will not pose a big problem for the deterministic world of computers since they speak the same language. As a matter of fact, today there are computer programs that perform quantitative data analysis almost completely automatically and are frequently used in research.
However, it is very difficult to say the same for qualitative data analysis. Qualitative data analysis inherently consists of textual and visual elements. Although today’s developing technology makes it easier to process text and visual elements, at the same time, in qualitative data analysis, researchers’ perspectives and interpretations are part of the analysis, and the same data can be handled in different ways by different researchers.

Created by DALL-E
The Rise of Chatbots and ChatGPT
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) have led to the increasing integration of chatbots into daily life. The journey of chatbots began in 1966 with Joseph Weizenbaum’s creation at MIT, initially designed to mimic a psychotherapist. The 2000s saw the rise of text-based robots on websites. By the 2010s, their use became widespread, particularly on e-commerce platforms. The recent years have marked a pinnacle in this evolution with the remarkable success of ChatGPT-3 and 4. We are likely still in the early stages of this technological development.
ChatGPT is being developed by OpenAI and it’s built on the GPT-4 architecture. GPT-4 is based on a neural network architecture called “Transformer”. These models are very effective for understanding the complexity and context of the language. ChatGPT is trained with a huge amount of training data collected from books, articles, websites and many other sources, and offers a versatile use with Natural Language Processing technologies. At the same time, ChatGPT continues to train itself continuously through user interactions. The combination of all this technology enables ChatGPT to work effectively on complex language tasks and allows it to have natural, meaningful and informative conversations with users.
ChatGPT has a serious use especially in digitally driven businesses. It can successfully perform many different tasks, from copywriting to advertising, from detecting errors in a program code to translating different languages into each other. But this day in the rest of our article, we will examine the competence of ChatGPT in qualitative data analysis, which people are perhaps most needed.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Source of Data
When starting data analysis, we should first talk about our dataset. After a short search on kaggle.com, we chose a dataset called “Famous Words Twitter Dataset“. To be honest, we did not have many criteria when deciding on the dataset. We wanted to see if Chat GPT could produce results with data that has not been studied much. In this context, we decided to use a dataset called Famous Words Twitter Dataset, which contains approximately 130,000 tweets collected with reference to different keywords.
130,000 tweets is too many for us. Therefore, again using ChatGPT, we eliminated this data with the keywords Covid-19 and Vaccine, leaving 10,000 tweets.
Identification and Cleansing of Data
We still have a lot of tweets, but we will do more sifting together. First of all, we will use the Data Analysis plugin provided by ChatGPT-4 for the whole process. We first send the data we keep as an excel file to the Data Analysis plugin and ask our first question; “What is this data about?”
ChatGPT gave us a summary of what this dataset contains. We then asked it which keywords were in the dataset and got the correct answer. If you remember, we limited our dataset to the keywords COVID-19 and Vaccine.
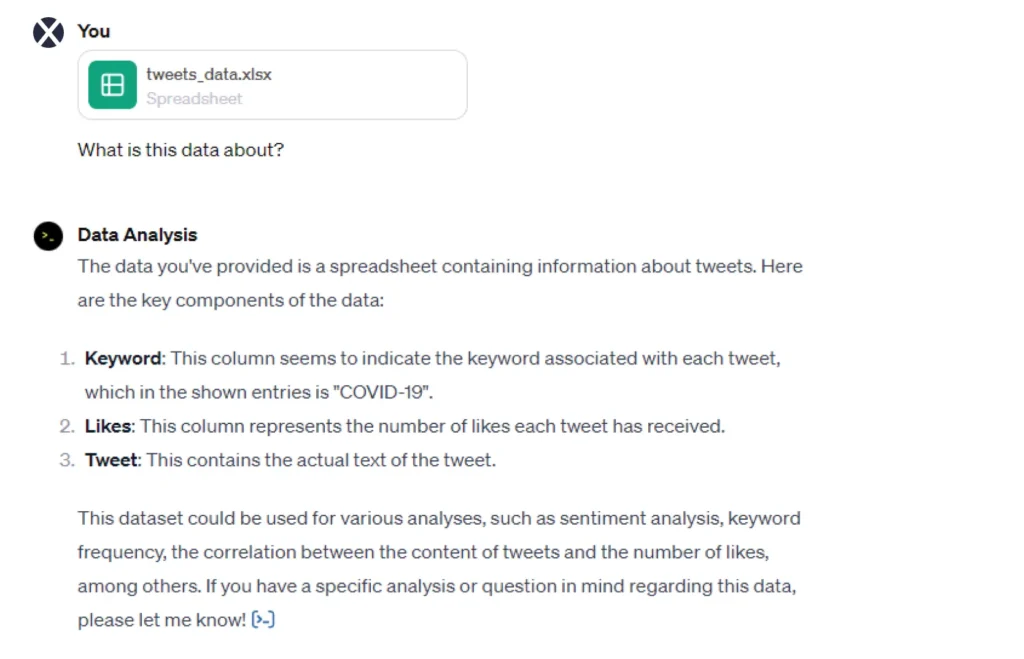
Now we tell Data Analysis to delete the data with the keyword Vaccine from the dataset. After eliminating the data with the Vaccine keyword, 5001 tweets remain. These commands are very easy for ChatGPT’s data analysis capabilities. It’s time to make things a little more difficult.
Let’s Start Qualitative Data Analysis with ChatGPT
Our first request to Chat GPT is to identify three main themes for qualitative data analysis, and to choose these themes from the most frequently encountered themes in the data set. Scientists and researchers usually come up with these themes themselves, and it is a very painful process. This paper is not an academic paper, so there is no problem for ChatGPT to help us.
We then asked ChatGPT to tag the tweets with the themes it had identified and to create a new excel file and send it to us. Obviously, we still don’t trust it at this stage and we check ourselves to make sure that the tweets are tagged with the correct themes. ChatGPT’s tagging was mostly accurate, but it did make some mistakes with some tweets that were single words or really meaningless. We can ignore these because our dataset is extremely unhealthy and has not been previously curated.

Once we have identified our main themes, the next thing we need to do is to identify the sub-themes under these main themes. For this, we first told ChatGPT something like “Taking the data labeled with “Policy and Government Response” from these themes, we need to create 3 sub-themes where these data meet in common.” When it did this perfectly, we asked it to do the same analysis for the other two themes and create sub-themes.


At this stage, we want to step out of qualitative data analysis and deal with quantitative data. We ask ChatGPT for the number of tweets tagged with themes and sub-themes and ask it to show them to us as bar graphs. It generates our graphs in a few seconds without any difficulty.
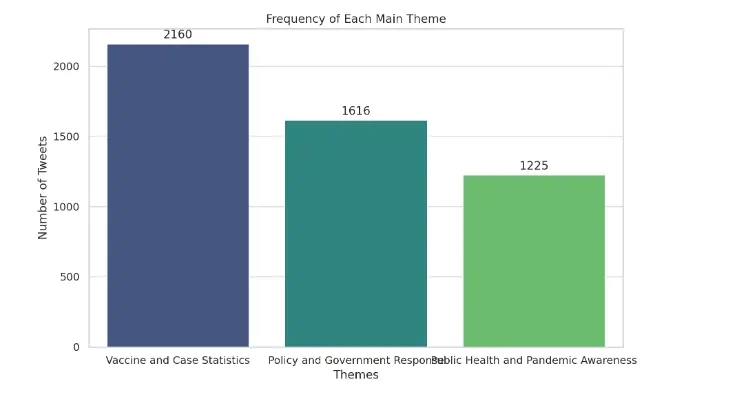
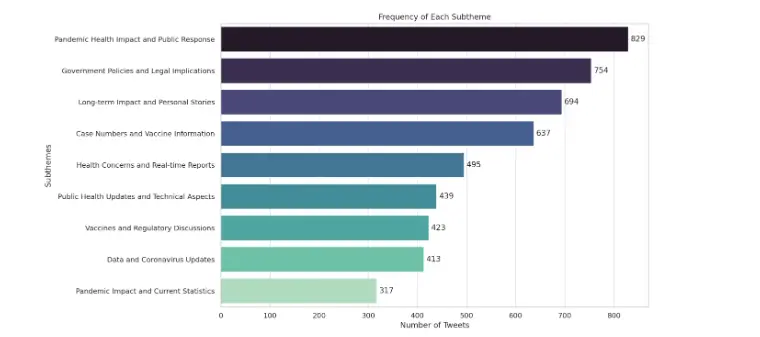
Going back to our qualitative data analysis, we mentioned that in qualitative data analysis, data belonging to themes are shown with quotations. To achieve this, we ask ChatGPT to show us the three tweets that best reflect the sub-theme for each of the sub-themes it has created. Here again, we are confronted with the fact that when tagging themes, it also tags tweets that consist of a single word or are really meaningless. A few tweets in the examples it sent are exactly like this. Here are some examples of sub-themes;

At this stage, we are confident that ChatGPT cannot perform a qualitative data analysis for an academic paper from start to finish. In fact, when we asked about it, it gave a similar answer, saying that it couldn’t do it. Still, it’s a great assistant. ChatGPT can produce results much faster than the standard desktop software that is often used in qualitative data analysis, which is actually completely human-interventionist.
But does ChatGPT have the ability to make inferences? To find out, after all these analyses, we ask it to prepare a 2000-word report written as it sees fit. ChatGPT produces a result that surprises us here. It produces an analysis report with a serious structure rather than a report like a simple blog post. But first it gives us detailed information about the structure of the report.You can download and review the PDF of the first analyze report with 2000 words by ChatGPT from this link.

Although the structure of the report looks great, the report is not detailed enough because we limited it to 2000 words. After ChatGPT prepares a report according to this structure, it informs us about the problem of not enough detail due to this 2000 words. So we ask it to expand the report. You can download and review the PDF of the expanded report from this link.
In the report, ChatGPT describes the stages of analysis, methodology, data generated by quantitative and qualitative methods. In the discussion section, it talks about the multifaceted nature of public opinion. It underlines the impact of social media in shaping public opinion. It even provides references. Of course, it makes some mistakes. For example, it suggests that the conversations in tweets have a complex texture based on the variety of sub-themes it created entirely at our request. When we tried it with fewer subthemes, it doesn’t mention this at all.
When analyzing data with ChatGPT in an academic paper, it is useful to think of it as an assistant. AI is not yet perfect enough to make decisions and interpretations on behalf of humans. Of course, it can do these things, but this can create problems both in terms of ethical debates and accuracy.
Literature Review with ChatGPT
Finally, we tell ChatGPT that we want to write an article as a result of these analyzes and we ask them to do a literature review to help us. You can access the answer to ChatGPT’s literature review from this link. In our experiment we found many relevant sources, we checked some of them and found that the sources were correct. It’s great that it presents it to us in a systematic and understandable language. Of course, it is not easy to do a full literature review for a scientific paper. Please keep in mind that such a literature review is the result of many days of work by researchers.
Discussion and Conclusion
ChatGPT can also create diagrams between themes, give you detailed information about the techniques it uses during analysis, and translate your data and charts into different languages. It will also often warn you about ethical values. We are sensitive about this too. Remember that writing a scientific paper is a very painful, labor-intensive and knowledge-intensive process, even for scientists who have spent years in this field. Artificial intelligence applications like ChatGPT can help you with this, but it is too early to rely on it completely.
In conclusion, ChatGPT’s applications in the field of qualitative data analysis show that this technology is more than just an interactive chat tool. The examples and analyses presented throughout our paper demonstrate ChatGPT’s capacity to make deep sense of text-based data, illuminate complex themes, and interpret human experiences in a digital format. This offers researchers, marketers and data analysts insights and meanings that are difficult to achieve with traditional methods. ChatGPT expands the boundaries of qualitative data analysis and makes this process more accessible, fast and effective. Going forward, we can expect this capacity of AI to develop further, transforming the nature and applications of qualitative data analysis. In light of these exciting developments, the future of ChatGPT and similar technologies opens new horizons not only in the field of data analysis, but also in our understanding of human knowledge and experiences.
Don’t forget to follow us on our social media accounts!



